A protein that behaves abnormally within a cell can contribute to disease. To understand how a disease is initiated and progresses over time, these proteins need to be identified and studied. Given that cells contain thousands of proteins, distinguishing between disease-causing and normal proteins is a difficult task.
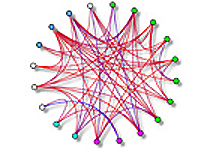
To address this, a team led by Dr. Igor Jurisica (PM Senior Scientist and Techna Core Lead) has developed a new computational method known as differential graphlet community that uses specialized maps (networks) that describe how proteins, within a particular type of cell, work together. Dr. Jurisica's approach compares networks from healthy and diseased cells to identify and characterize differences between them.
Using this new method, researchers compared networks between healthy and cancerous lung tissue and identified several relationships between proteins that only occur in the cancerous tissue. These results were confirmed by Dr Jurisica's team using the same method with an independent set of healthy and cancerous lung tissue. The results were in agreement with previous work, carried out by other researchers that used different experimental methods.
These findings suggest that the differential graphlet community approach can be used to uncover new protein relationships that are involved in diseases and to identify new potential targets to treat these diseases. Furthermore, given that this approach computational in nature, it could be generalized and used to gain insight into other diseases and conditions.
This work was supported by the Ontario Research Fund, the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the Canada Foundation for Innovation and The Princess Margaret Cancer Foundation. I Jurisica holds a Tier 1 Canada Research Chair in Integrative Cancer Informatics.
Comparative network analysis via differential graphlet communities. Wong SW, Cercone N, Jurisica I. Proteomics. 2014 Oct 6. [Pubmed abstract]




Comments