
April 2015 | mcewencentre.com
Beta Cells
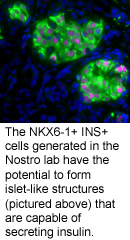
Individuals with type 1 diabetes are unable to regulate blood glucose because their insulin-secreting pancreatic beta cells have been destroyed by the immune system. Studies suggest that replacing these lost cells with stem cell-derived beta cells might reverse this effect. However, reproducible methods for generating large populations of stem cell-derived beta cells are currently lacking because the complex pathways that control pancreatic cell development are not well defined.
A new study led by McEwen Centre Researcher Dr. Maria Cristina Nostro has advanced this area of research by revealing key pathways that regulate the differentiation of human pluripotent stem cell (hPSC)-derived pancreatic progenitor cells.
Previous studies by Dr. Nostro provided a protocol for the generation of hPSC-derived pancreatic progenitors that is dependent on treatment with key growth factors such as retinoic acid and fibroblast growth factor 10, as well as inhibition of bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) and hedgehog signalling pathways. Treatment of these progenitors with inhibitors of TGFβ signalling leads to the generation of cells that lack NKX6-1 expression and are non-glucose responsive.
Dr. Nostro’s current study revealed that activation of the epidermal growth factor and nicotinamide signalling pathways generates NKX6-1+ cells that have the potential to differentiate into beta-like cells in vivo. Importantly, the study revealed that the size of the NKX6-1+ population is affected by the duration of treatment with retinoic acid and fibroblast growth factor 10, as well as treatment with the inhibitors of BMP and hedgehog signalling pathways.
These key findings define—for the first time—the pathways that regulate the development of NKX6-1+ progenitors. They also provide a strategy for generating highly enriched populations of these cells, which can be used to uncover the pathways that regulate the maturation of hPSC-derived beta cell progenitors into functional pancreatic beta cells.
This work was supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia, the Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation, Stem Cells Australia and the Victorian Government's Operational Infrastructure Support Program and the Toronto General & Western Foundation. G Keller holds a Tier 1 Canada Research Chair in Embryonic Stem Cell Biology and MC Nostro is the McEwen Centre for Regenerative Medicine Harry Rosen Chair in Diabetes and Regenerative Medicine Research. Image courtesy of MC Nostro.
Efficient generation of NKX6-1+ pancreatic progenitors from multiple human pluripotent stem cell lines. Nostro MC, Sarangi F, Yang C, Holland A, Elefanty AG, Stanley EG, Greiner DL, Keller G. Stem Cell Reports. 2015 Apr 1. [Abstract]
 Congratulations to Dr. Andras Nagy on the successful renewal of his Tier I Canada Research Chair in Stem Cells and Regeneration. The award will support Dr. Nagy’s research, which aims to improve our understanding of human development by uncovering the pathways that regulate pluripotency and stem cell self-renewal.
Congratulations to Dr. Andras Nagy on the successful renewal of his Tier I Canada Research Chair in Stem Cells and Regeneration. The award will support Dr. Nagy’s research, which aims to improve our understanding of human development by uncovering the pathways that regulate pluripotency and stem cell self-renewal.

The University of Toronto’s Department of Chemical Engineering & Applied Chemistry, in partnership with the Institute of Biomaterials & Biomedical Engineering, will be hosting a symposium to honour Dr. Molly Shoichet’s appointment to the rank of University Professor on Thursday June 4th. A host of experts, including Drs. Cindi Morshead (University of Toronto), Kevin Healy (University of California, Berkley) and Jeff Karp (Harvard Medical School), will present their research on new innovations in bioengineering and regenerative medicine at the event. The symposium will culminate with a presentation by Dr. Shoichet titled ‘Imagination and innovation: biomimetic hydrogels for 3D cell culture’. For more information on this event, click here.
The antidiabetic hormone glucagon-like peptide-1 induces formation of new elastic fibers in human cardiac fibroblasts after cross-activation of IGF-IR. Qa'aty N, Wang Y, Wang A, Mao S, Vincent M, Husain M, Hinek A. Endocrinology. 2015 Jan. [Abstract]
The expression of dominant negative TCF7L2 in pancreatic beta cells during the embryonic stage causes impaired glucose homeostasis. Shao W, Xiong X, Ip W, Xu F, Song Z, Zeng K, Hernandez M, Liang T, Weng J, Gaisano H, Nostro MC, Jin T. Mol Metab. 2015 Feb 4. [Abstract]
Synergetic use of neural precursor cells and self-assembling peptides in experimental cervical spinal cord injury. Zweckberger K, Liu Y, Wang J, Forgione N, Fehlings MG. J Vis Exp. 2015 Feb 23. [Abstract]
Transgenic mice for intersectional targeting of neural sensors and effectors with high specificity and performance. Madisen L, Garner AR, Shimaoka D, Chuong AS, Klapoetke NC, Li L, van der Bourg A, Niino Y, Egolf L, Monetti C, Gu H, Mills M, Cheng A, Tasic B, Nguyen TN, Sunkin SM, Benucci A, Nagy A, Miyawaki A, Helmchen F, Empson RM, Knöpfel T, Boyden ES, Reid RC, Carandini M, Zeng H. Neuron. 2015 Mar 4. [Abstract]
Efficient generation of NKX6-1+ pancreatic progenitors from multiple human pluripotent stem cell lines. Nostro MC, Sarangi F, Yang C, Holland A, Elefanty AG, Stanley EG, Greiner DL, Keller G. Stem Cell Reports. 2015 Apr 1. [Abstract]
Click-crosslinked injectable hyaluronic acid hydrogel is safe and biocompatible in the intrathecal space for ultimate use in regenerative strategies of the injured spinal cord. Führmann T, Obermeyer J, Tator CH, Shoichet MS. Methods. 2015 Apr 3. [Abstract]
A novel polymeric drug delivery system for localized and sustained release of tacrolimus (FK506). Tajdaran K, Shoichet MS, Gordon T, Borschel GH. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2015 Apr 7. [Abstract]
Mechanical stress promotes maturation of human myocardium from pluripotent stem cell-derived progenitors. Ruan JL, Tulloch NL, Saiget M, Paige SL, Razumova MV, Regnier M, Tung KC, Keller G, Pabon L, Reinecke H, Murry CE. Stem Cells. 2015 Apr 11. [Abstract]
Genetic conflict reflected in tissue-specific maps of genomic imprinting in human and mouse. Babak T, DeVeale B, Tsang EK, Zhou Y, Li X, Smith KS, Kukurba KR, Zhang R, Li JB, van der Kooy D, Montgomery SB, Fraser HB. Nat Genet. 2015 Apr 13. [Abstract]
The McEwen Centre for Regenerative Medicine, led by director Dr. Gordon Keller, includes 15 scientists at the University of Toronto and five Toronto hospitals, working to advance the development of more effective treatments for conditions including heart disease, diabetes, respiratory disease and spinal cord injury.
The Centre is located at University Health Network, MaRS Centre, Toronto Medical Discovery Tower, 101 College Street, 8th Floor, Room 701, Toronto, Ontario, Canada M5G 1L7
Email: mcewencentre@uhn.ca
Feedback/To Unsubscribe
McEwen Monthly is brought to you by the McEwen Centre for Regenerative Medicine and UHN Research Communications. We hope you have enjoyed receiving this message. If you have any feedback, or if you would prefer to receive the newsletter in text format, please email mkinyanj@uhnresearch.ca.