It happens during a long day of sitting in the office, while cramped into your seat on long-haul flights, and it can harm your health.
During periods of inactivity, fluids pool in your lower legs. This can lead to serious health issues, including the formation of blood clots in the leg, which if left untreated can cause a life-threatening condition known as a pulmonary embolism.
As well as being harmful during the day, the pooled fluids can cause havoc when you lie down at night. The fluids shift from the lower extremities towards the head, where they can obstruct breathing and worsen conditions such as sleep apnea, a disorder in which breathing slows or stops for minutes at a time during sleep.
Wearing compression stockings can help prevent pooling of blood in the legs. However, for those with spinal cord injuries and the elderly, compression stockings can be difficult to put on and remove and many people report discomfort while wearing them. Thus, most of the people who may benefit from compression stockings don’t use them.
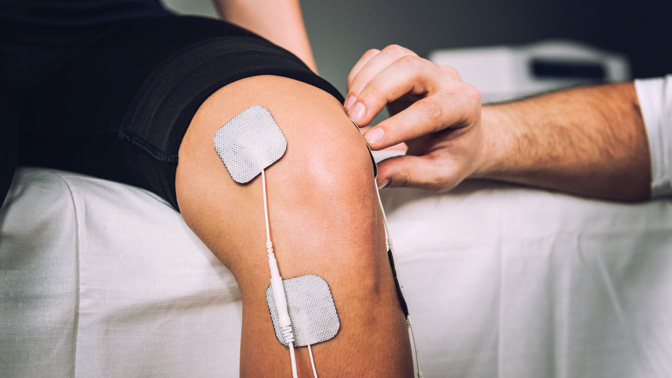
To address this problem, TRI Scientist Dr. Azadeh Yadollahi explored a new therapy to prevent fluid buildup that uses electrical stimulation to make the calf muscles in the leg contract.
Dr. Yadollahi’s team was particularly interested in whether the new therapy could help those with sleep apnea. With this in mind, her team enrolled 13 men with sleep apnea. The chosen study participants were free from other chronic or debilitating illnesses, had normal blood pressure and were not obese.
In order to test whether the new therapy was effective, fluid buildup in the legs of participants was measured as they sat stationary for 150 minutes during two separate sessions. In one session, the electrical therapy was applied; while in the other session, participants received a mock therapy.
The results revealed that after 150 minutes of electrical stimulation, fluid buildup was reduced by 43%. Furthermore, swelling of the legs (measured as a change in calf circumference) was reduced by almost 90%.
“Our findings show that electrical stimulation of the calf is a promising strategy to prevent leg fluid accumulation. The improvements that we observed, when compared to previous studies, suggest that our approach has the potential to reduce the severity of sleep apnea by around a third,” said Dr. Yadollahi.
Future work will focus on developing the approach into a compact and easy to use therapeutic device—one that could help a wide range of individuals affected by leg fluid buildup, including office workers, cashiers, flight attendants, frequent flyers, and those suffering from sleep apnea and spinal cord injuries.
This work was supported by the Toronto Rehab Foundation.
The Effect of Electrical Stimulation of the Calf Muscle on Leg Fluid Accumulation over a Long Period of Sitting. Vena D, Rubianto J, Popovic MR, Fernie GR, Yadollahi A. Sci Rep. 2017 Jul 20;7(1):6055. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-06349-y.

Published in Scientific Reports and led by Dr. Azadeh Yadollahi (pictured), the study reveals a new way to prevent the harmful buildup of fluid that occurs during prolonged sitting.